-
Failure Detection Techniques on the Demand Side of Smart and Sustainable Compressed Air Systems: A Systematic Review
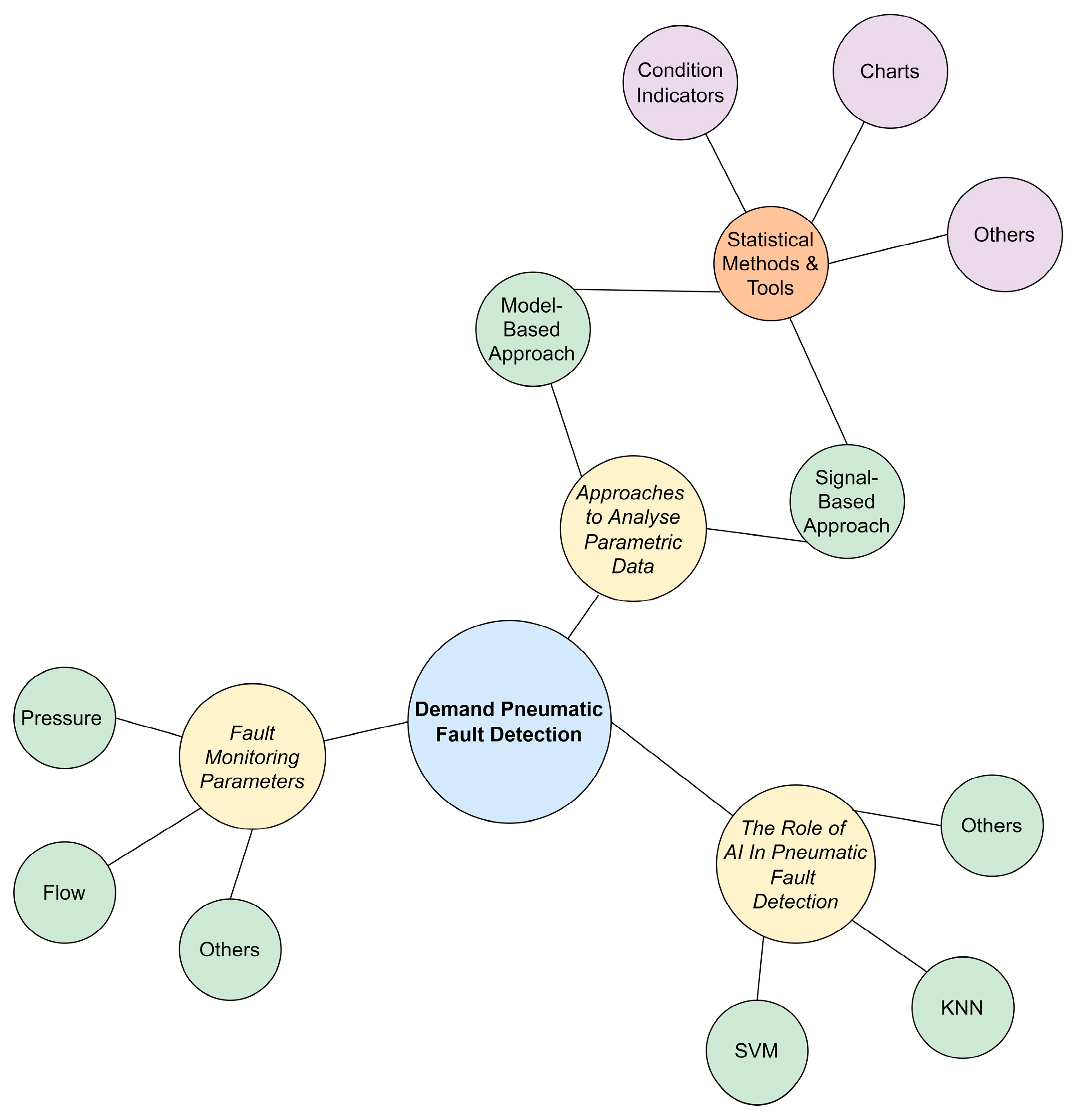
This paper offers a novel review based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) methodology of fault detection methods on the demand side of compressed air systems, leading towards a comprehensive understanding of smart and sustainable pneumatic systems. Fifty-three studies were classified and reviewed under the following three areas: (a) demand parameters which help in identifying fault sources; (b) approaches taken to analyse the parametric data; and (c) the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in pneumatic fault monitoring systems. This review shows that fault detection on the demand side has received greater importance in the last five years and that data analysis is crucial for AI to be implemented correctly.
Intelligent Approaches for Anomaly Detection in Compressed Air Systems: A Systematic Review
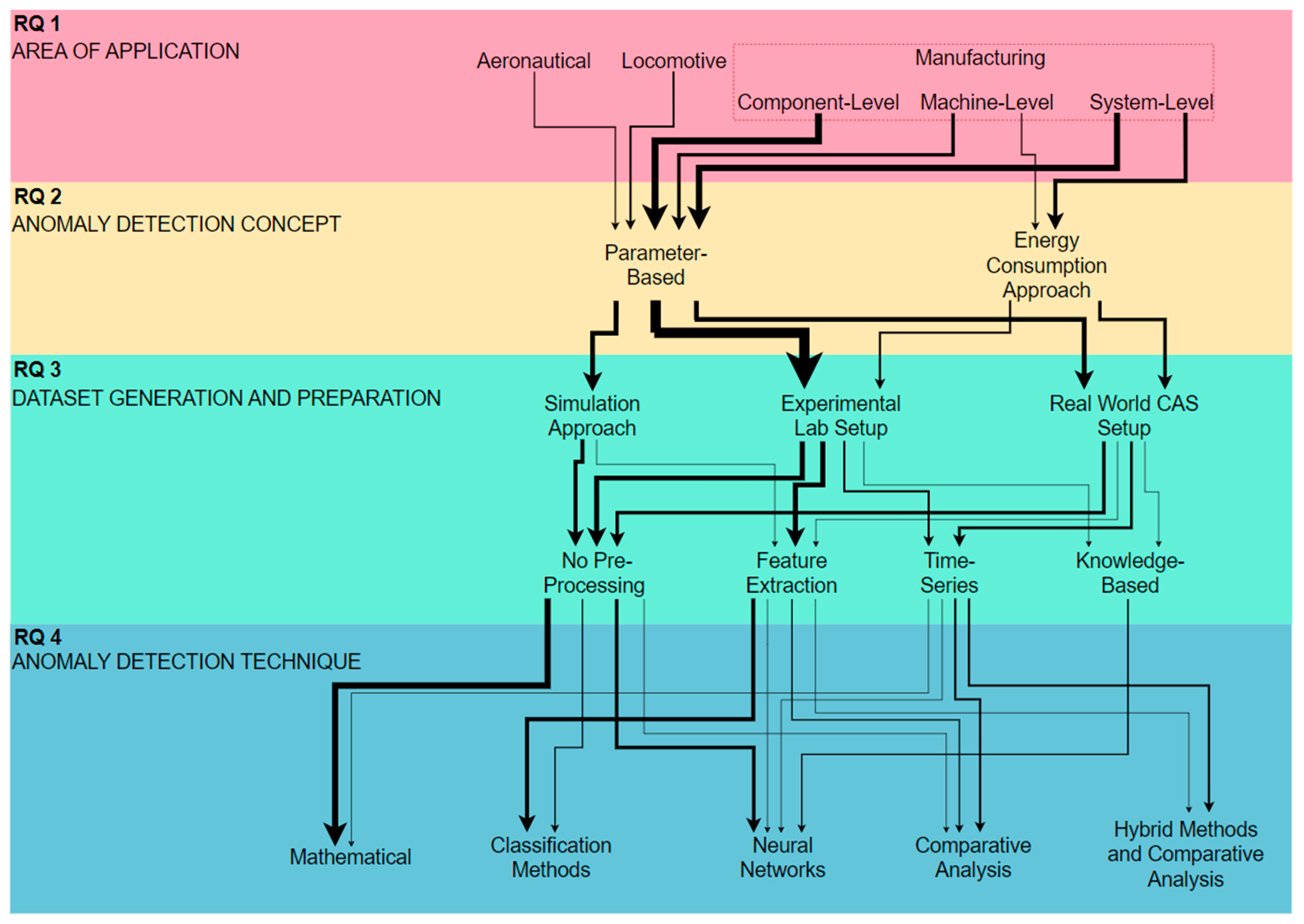
A systematic literature review of intelligent approaches within CASs was carried out, in which the research methodology was based on the PRISMA guidelines. The search was carried out on 1 November 2022 within two databases: Scopus and Web of Science. The research methodology resulted in 37 papers eligible for a qualitative and bibliometric analysis based on a set of research questions. These aimed to identify specific characteristics of the selected publications. Thus, the review performed a comprehensive analysis on mathematical approaches, multiple machine learning (ML) methods, the implementation of neural networks (NNs), the development of time-series techniques, comparative analysis, and hybrid techniques.
Autonomous Fault Monitoring for Efficient Multi-Actuator Compressed Air Systems: Data Analytics of Demand-Oriented Parameters
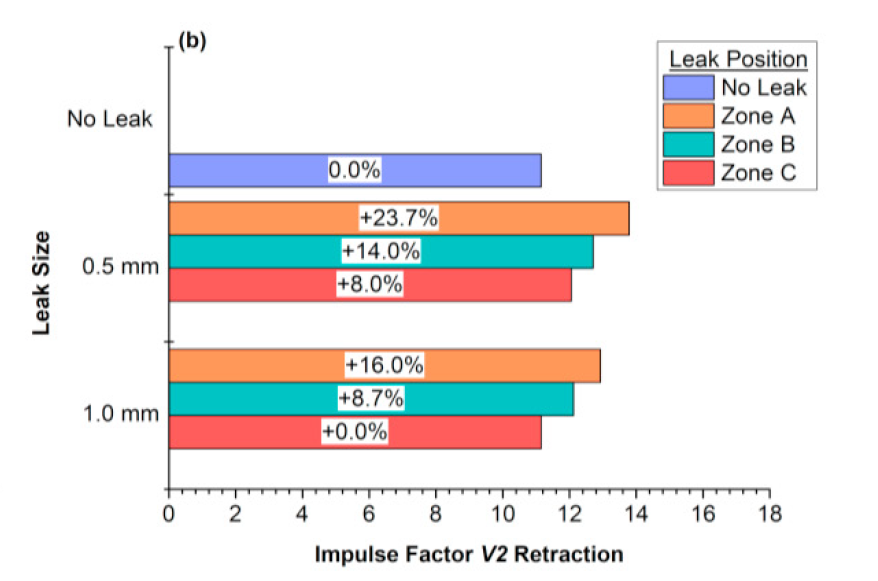
Studies covering pneumatic fault monitoring typically perform research on simple systems, investigating the effects on a single actuator or a very small system. This study aimed at tackling this issue, with tests performed on an industrial multi-actuator pick-and-place setup, logging data (i.e. cycle time, flow rate and system pressure) concurrently at two locations within the system. Furthermore, different sized leaks were introduced at three distinct locations, while monitoring their impacts on the system. It was found that with the use of the average, standard deviation and impulse factor of the cycle time and the other two parameters, it was possible to identify the presence of faults on a relatively large system. For instance, the retraction time for one of the actuators reduced by 26% as one of the faults was induced. With modern industrial setups already logging the cycle time and system pressure along the demand-side, this study shows that by using existing equipment, one can develop a reliable fault monitoring system.
Implementation of an intelligence-based framework for anomaly detection on the demand-side of sustainable compressed air systems
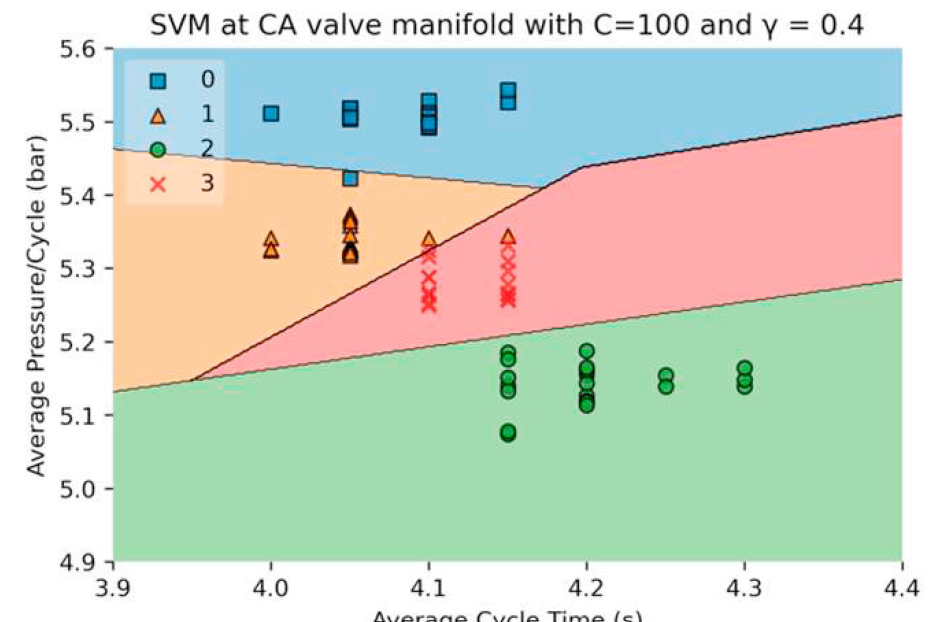
The implementation of intelligent techniques produces good results in automating fault finding and predicting future outcomes. These approaches have been on the increase in the past years, especially so to detect faults within Compressed Air Systems (CASs). With the use of intelligent techniques, one could minimise the manual and time-consuming aspect of CAS maintenance, improve the environmental impact of the system, while minimising downtime. This paper proposes a general framework for the implementation of intelligent analysis techniques within a real-world system. Such an approach has been implemented on the demand-side of a CAS. In literature, no open datasets are available for use by artificial intelligence models. Hence, as part of this research, a fault generating and monitoring system has been connected to an existing production machine in a manufacturing site to collect the required data. Two classification machine learning methods were implemented and compared across a number of performance metrics.
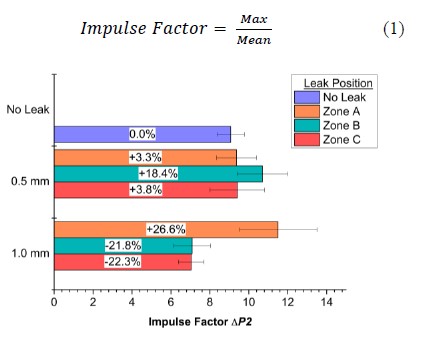
Fault Condition Indicators along the Demand Side of a Sustainable Compressed Air System
The goal of this study was to identify parameters which can be used to computationally detect the presence of faults in a pneumatic pick-and-place system within an industrial automation setup. Leakages and pressure drops were systematically induced at three locations along the demand side of the system. Pneumatic data was collected from two separate locations simultaneously, and this work presents the systematic approach utilised to
investigate the impacts of each fault. Indicators, namely the mean, standard deviation and impulse factor for pressure and flow rate data were
identified as being able to identify the presence of faults together with their severity, type and location.
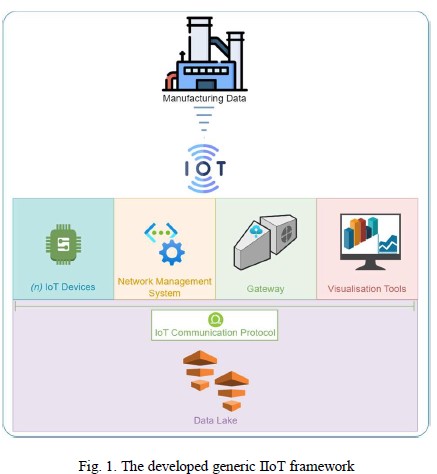
The development of a generic IIOT framework for an
industrial pneumatic system
This paper proposes a generic IIoT framework for the online real time monitoring of system parameters. Such an approach has been implemented on the demand-side of a pneumatic setup, and a visualisation technique was developed for evaluation purposes. The developed framework paves the way towards further data analytics with the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques.
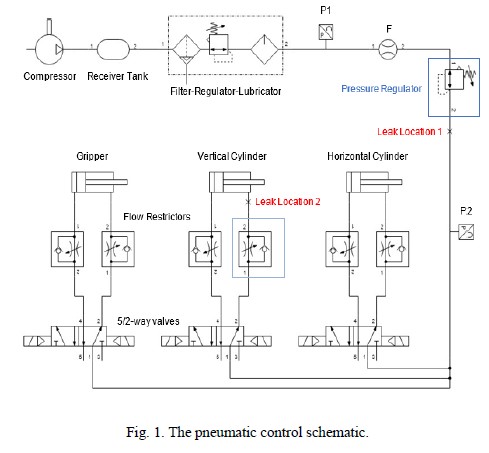
Pneumatic Control for Sustainable Compressed Air Systems: Multi-criteria Optimisation for Energy Efficient Production
This study focused on identifying the effects of pressure and flowrate regulation on the energy efficiency and productivity of a pneumatic automation system. By combining these two control strategies, a reduction in air consumption was achieved while also maintaining the system’s cycle time in order to minimise productivity loss. The assessed system included various leaks of different sizes at different locations. When implementing pressure regulation, a reduction in air consumption of up to 22 per cent was achieved.
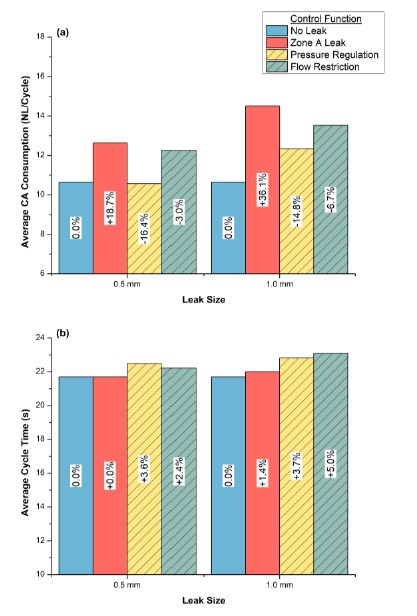
Pneumatic Fault Monitoring and Control for Sustainable Compressed Air Systems
This study
shows how fault monitoring was performed on a multi-actuator system, using different time domain indicators including, mean and standard
deviation. This was followed by exploring the system behaviour when pressure and flowrate control strategies were executed to minimize fault
impacts. Fault monitoring, using the indicator data, was successful. For instance, as a 1 mm leak was induced and the consumption increased by
34%, the standard deviation in pressure drop reduced by 6% and the mean actuation time decreased by 13%.
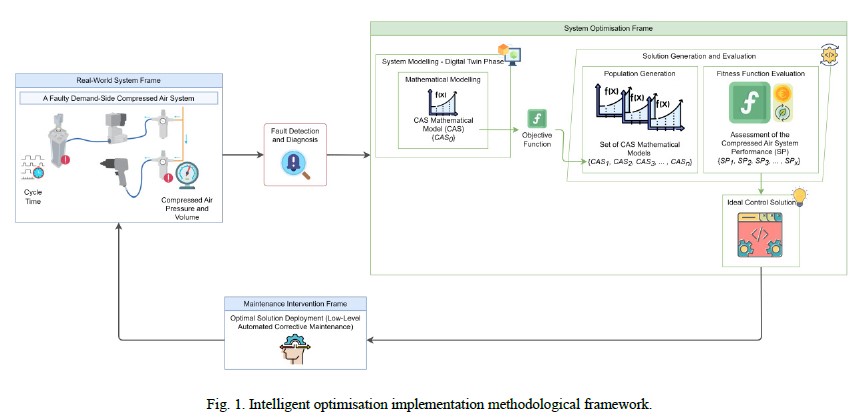
Intelligent optimisation in smart and sustainable compressed air systems: Towards support for decision-making under faulty conditions
The proposed solution uses intelligent optimisation techniques to identify the ideal control solution within these complex systems when faults arise.
This paper presents a framework based on an intelligent optimisation approach, which provides a workflow process for the support of decisionmaking
during faulty situations. It is adapted and implemented to the demand-side of a Compressed Air System (CAS), thus providing a holistic
approach in automating fault mitigation during real-time system operation. In implementing this framework, multiple intelligent optimisation
techniques such as the Genetic Algorithm and the Particle Swarm Optimisation algorithms were adopted and implemented. Both algorithms were
successful in providing the ideal control solution under fault conditions.